Head lice are tiny parasitic insects that can be found on human head. They don’t have wings so typical to other insects. They move thanks to three pairs of claw-like legs that are adopted to strong grips of the hair. Lice feed only on human blood.
The body of lice is an oval shape, elongated and dorsoventrally flattened. Their mouth parts are highly adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. The abdomen area have pairs of spiracles thru which the insects breath. The larvaes are 2-3 mm long and the adult louse are about 4 mm long.
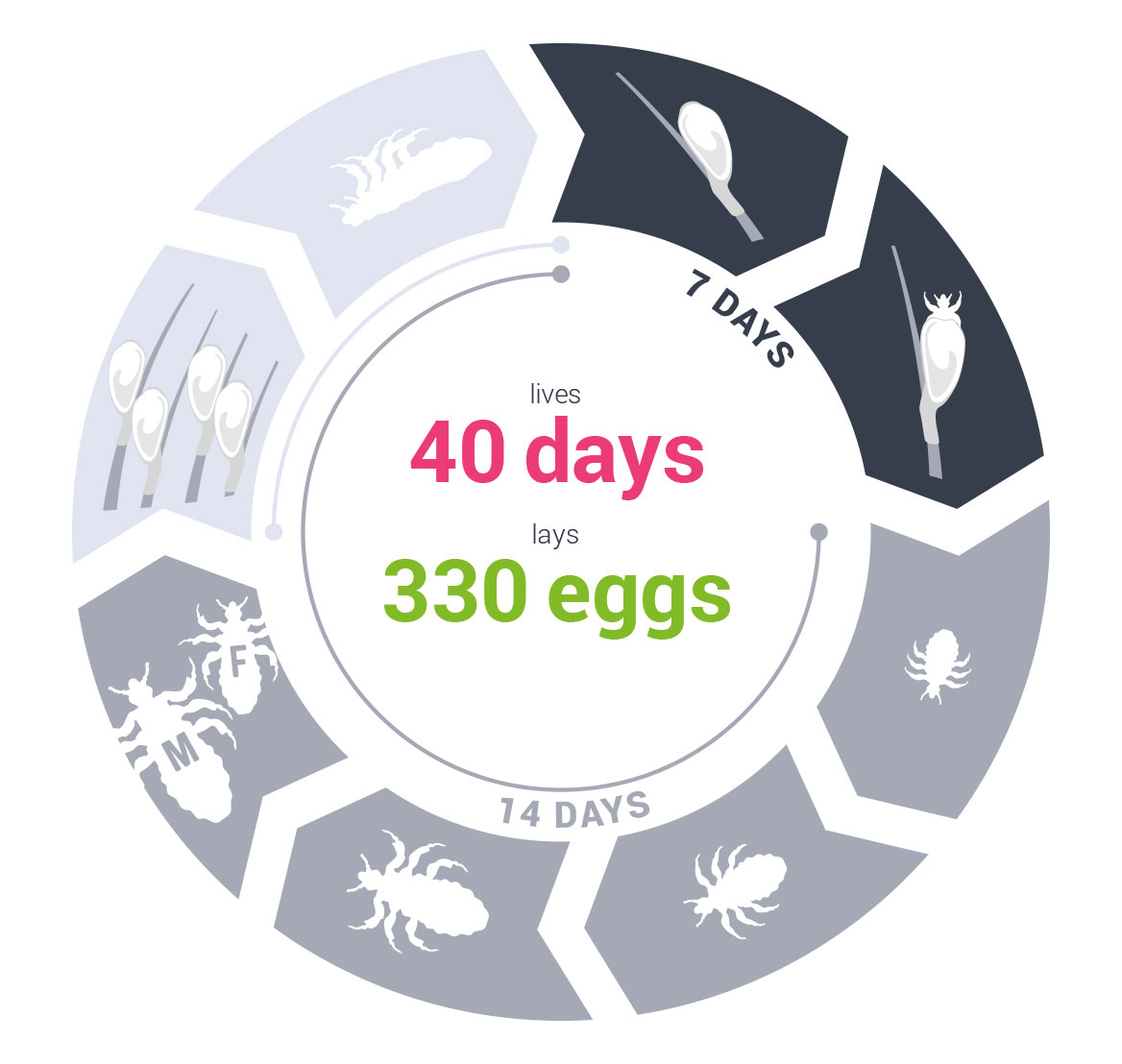
Lice eggs called nits are white or pearl in color and about 0.8 cm long. Immediately after nits are layed, the female attaches them to the hair shaft using special cement-like material. Nits can survive without the host up to 2 weeks and be a source of infestation. Effective 100% elimination of nits is crucial in the treatment of head lice infestation. An important part of the treatment is also a mechanically removal of nits from the hair by combing with a fine-tooth comb.
The female head louse lives about 40 days and lays about 300 eggs during this time (about 8 eggs a day). Nits take about 7 days to hatch and release nymphs. The nymph looks like an adult head louse and it feeds on a human blood as well. After about 2 weeks the nymph is fully mature and able to reproduce. Nymph and adult louse may survive without the host for up to 2 days.
Head lice live only on human scalp. They can’t jump nor fly, they don’t get transmitted by household animals. They can only be spread by direct contact with the infested person. Thus, to move from one head to another, the lice wait till the contact of two people heads occur. This happens quite often during playdates, camping or summer camps.
The infection can also easily occur at school, where lice have a good opportunity to spread. Lice can also be spread through sharing of personal items like combs, brushes, hair bands, pillows, towels, hats, scarves and clothes.
Confirmed diagnosis of head lice infestation is stressful and very difficult for both children and parents. It is a common problem that can touch anyone. All you have to do is to act quickly and effectively.
Remember that the successful treatment would be only achieved by conducting simultaneous treatment of all infected people. Therefore, do not hide the problem and notify all parents of your children’s friends about a possible infection.
Head lice are scavengers and they feed on human’s blood only. They cannot fly or jump.